|
While talking to a distant subscriber on
telephone, quite often we feel frustrated when the voice of the distant subscriber is so
faint that it is barely intelligible. To overcome the problem, circuit of an inexpensive
amplifier is presented here. It can be assembled and tested easily. There is no extra
power source needed to power up the circuit, as it draws power from the telephone line
itself. The amplifier will provide fairly good volume for the telephone conversation to be
properly heard in a living room. A volume control is included to adjust the volume as
desired.
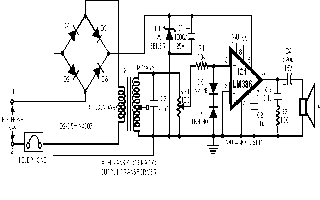
The circuit is built around IC LM386. Diodes D6 and D7 are used to
limit the input signal strength. Transformer X1 is a transistor radio's output
transformer used in reverse. As
original secondary (output) winding
is connected in series with the telephone lines, the speech signals passing through the
lines cause change in the magnetic flux in the core of transformer and thereby induce
signal voltage across the primary winding. This audio signal is used as input for IC
LM386.
Diodes D2 through D5 connected in bridge configuration constitute a
polarity guard so that the amplifier is powered with correct polarity, irrespective of the
line polarity, Zener
diode D1 may have any breakdown
voltage between 6 and 12 volts
range. e.
|
|
There is no need of a separate power switch as the
circuit energises (via the normally open contacts of the cradle switch) when one lifts the
handset.
The circuit may be wired on a general-purpose PCB or by etching a PCB for this circuit.
The circuit can be easily tested by connecting a 6 volts supply to line
terminals 1 and 2. A hissing sound will be heard from the loudspeaker. Now connect 6V AC
from a transformer to terminals 1 and 2 and observe hum in the loudspeaker. The volume of
the hum can be changed through potentiometer VR1. Diodes D6 and D7 limit the input below
± 700 mV.
The circuit is to be connected to the telephone lines in series with the telephone
instrument, as shown in the figure |