Phono Preamplifier
Simple circuitry suitable for moving-magnet cartridges
Passive high-frequency equalization
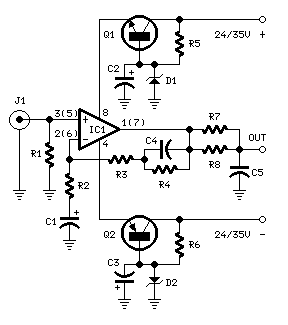
Parts:
R1_________47K 1/4W Resistor R2________100R 1/4W Resistor R3__________6K8 1/4W Resistor R4_________68K 1/4W Resistor R5,R6_______2K7 1/4W Resistor R7__________2K2 1/4W Resistor R8_________39K 1/4W Resistor C1-C3_____100µF 25V Electrolytic Capacitors C4,C5______47nF 63V Polyester Capacitors 5% tolerance D1,D2__BZX79C18 18V 500mW Zener Diodes IC1_______LM833 Low noise Dual Op-amp Q1________BC337 45V 800mA NPN Transistor Q2________BC327 45V 800mA PNP Transistor J1__________RCA audio input socket
Comments:
In recent years, following CD's introduction, vinyl recordings are almost disappeared. Nevertheless, a phono preamplifier is still useful for listening old vinyl discs from a well preserved collection. This simple but efficient circuit devised for cheap moving-magnet cartridges, can be used in connection with both audio power amplifiers shown in preceding pages, featuring low noise, good RIAA frequency response curve, low distortion and good high frequency transients behaviour due to passive equalization in the 1 to 20KHz range. Transistors and associated components provide ± 18V supply to the op-amp, improving headroom and maximum output voltage.
Notes:
-
R2, R3, R4, R7, R8, C4 & C5 should be low tolerance types.
-
Schematic shows left channel and power supply.
-
For stereo operation R1, R2, R3, R4, R7, R8; J1; C1, C4 & C5 must be doubled.
-
Numbers in parentheses show IC1 right channel pin connections.
Technical data:
Sensitivity @ 1KHz: 2.5mV RMS input for 200mV RMS output
Max. input voltage @ 1KHz: 120mV RMS
Max. input voltage @
10KHz: 141mV RMS
Max. input voltage @ 20KHz: 127mV RMS
Frequency response @ 1V RMS output: 100Hz to 20KHz ± 0.5dB;
-0.75dB @ 30Hz
Total harmonic distortion @ 1KHz and 6V RMS
output: 0.006%
Total harmonic distortion @10KHz and 1V RMS
output: 0.02%