MCA 16 bit bus
pinout
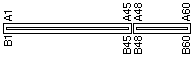 116 pin MCA bus connector at the motheboard | Micro Channel architecture (in practice almost always shortened to MCA) was a proprietary 16 or 32-bit parallel computer bus created by IBM in the 1980s for use on their new PS/2 computers. For a time MCA could be found in the PS/2, RS/6000, AS/400 and even some of the System/370 mainframes. However all of these later moved on to more capable, standards based, busses (such as PCI) and MCA is no longer used. MCA was primarily a 32-bit bus, but the system also supported a 16-bit mode which was primarily to lower the cost of connectors and logic in Intel-based machines like the PS/2. The situation was never that simple however, as both the 32-bit and 16-bit versions had a number of additional optional connectors which resulted in a huge number of physically incompatible cards. On the upside, MCA also moved the pins around to minimize interference, a ground or a supply was located within 3 pins of every signal. The data rate was increased from ISA"s 8MHz to 10, for a small improvement in performance. However the communications was now driven by the bus as opposed to the CPU, so real throughput was greatly increased, about four times, to 40MBps (of a theoretical 66). With bus-mastering the card could talk to each other directly so the performance was independent of the CPU. This led to possible collisions when more than one card would try to master, but MCA included an arbitration feature to correct for these situations, and also allowed a master to use a burst-mode where they had complete control for up to 12 milliseconds. Multiple busmaster support and improved arbitration means that several such devices can coexist and share the system bus. MCA busmasters can even use the bus to talk directly to each other at speeds faster than the system CPU, without any other system intervention. Arbitration enhancement also provides that we have better system throughput since control is passed more efficiently. Advanced interrupt handling refers to the use of level sensitive interrupts to handle system requests. Rather than a dedicated interrupt line, several lines can be shared to provide more possible interrupts. The final major improvement was POS, the Programmable Option Select, which allowed all setup to take place in software. This feature is taken for granted now, but at the time setup was a huge chore for ISA systems. POS was a simple system that included device ID"s in firmware, which the drivers in the computer were supposed to interpret. This is the basis of plug-and-play today. Although MCA was a huge improvement over ISA, it was limited only to IBM hardware. It was not compatible with either EISA or XT bus architecture so older cards cannot be used with it. This small market made for very high prices, and IBM didn"t help matters by charging high licensing fees. MCA was largely ignored, and with the introduction of PCI, MCA swiftly disappeared.
Source:www.pinouts.ru |