60W Guitar Amplifier
Bass, Treble, Harmonic modifier and Brightness controls
Output power: 40W on 8 Ohm and 60W on 4 Ohm loads
Amplifier circuit diagram:
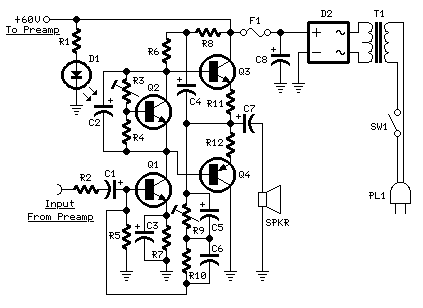
Amplifier parts:
R1__________________6K8 1W Resistor
R2,R4_____________470R 1/4W Resistors
R3__________________2K 1/2W Trimmer Cermet
R5,R6_______________4K7 1/2W Resistors
R7________________220R 1/2W Resistor
R8__________________2K2 1/2W Resistor
R9_________________50K 1/2W Trimmer Cermet
R10________________68K 1/4W Resistor
R11,R12______________R47 4W Wirewound Resistors
C1,C2,C4,C5________47µF 63V Electrolytic Capacitors
C3________________100µF 25V Electrolytic Capacitor
C6_________________33pF 63V Ceramic Capacitor
C7_______________1000µF 50V Electrolytic Capacitor
C8_______________2200µF 63V Electrolytic Capacitor (See Notes)
D1_________________LED Any type and color
D2________Diode bridge 200V 6A
Q1,Q2____________BD139 80V 1.5A NPN Transistors
Q3_____________MJ11016 120V 30A NPN Darlington Transistor (See Notes)
Q4_____________MJ11015 120V 30A PNP Darlington Transistor (See Notes)
SW1_______________SPST Mains switch
F1__________________4A Fuse with socket
T1________________220V Primary, 48-50V Secondary 75 to 150VA Mains transformer (See Notes)
PL1_______________Male Mains plug
SPKR______________One or more speakers wired in series or in parallel
Total resulting impedance: 8 or 4 Ohm
Minimum power handling: 75W
Preamplifier circuit diagram:
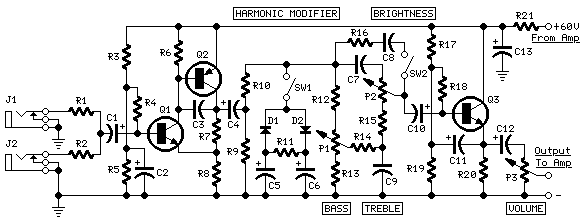
Preamplifier
parts:
P1,P2______________10K Linear Potentiometers P3_________________10K Log. Potentiometer R1,R2______________68K 1/4W Resistors R3________________680K 1/4W Resistor R4________________220K 1/4W Resistor R5_________________33K 1/4W Resistor R6,R16______________2K2 1/4W Resistors R7__________________5K6 1/4W Resistor R8,R21____________330R 1/4W Resistors R9_________________47K 1/4W Resistor R10_______________470R 1/4W Resistor R11_________________4K7 1/4W Resistor R12,R20____________10K 1/4W Resistors R13_______________100R 1/4W Resistor R14,R15____________47R 1/4W Resistors R17,R18,R19_______100K 1/4W Resistors C1,C4,C5,C6________10µF 63V Electrolytic Capacitors C2_________________47µF 63V Electrolytic Capacitor C3_________________47pF 63V Ceramic Capacitor C7_________________15nF 63V Polyester Capacitor C8_________________22nF 63V Polyester Capacitor C9________________470nF 63V Polyester Capacitor C10,C11,C12________10µF 63V Electrolytic Capacitors C13_______________220µF 63V Electrolytic Capacitor D1,D2____________BAT46 100V 150mA Schottky-barrier Diodes (see Notes) Q1,Q3____________BC546 65V 100mA NPN Transistors Q2_______________BC556 65V 100mA PNP Transistor J1,J2___________6.3mm. Mono Jack sockets SW1,SW2___________SPST Switches
Circuit description:
This design adopts a well established circuit topology for the power
amplifier, using a single-rail supply of about 60V and capacitor-coupling for
the speaker(s). The advantages for a guitar amplifier are the very simple
circuitry, even for comparatively high power outputs, and a certain built-in
degree of loudspeaker protection, due to capacitor C8, preventing the voltage
supply to be conveyed into loudspeakers in case of output transistors'
failure.
The preamp is powered by the same 60V rails as the power amplifier,
allowing to implement a two-transistors gain-block capable of delivering about
20V RMS output. This provides a very high input overload capability.
Technical data:
- Sensitivity:
-
35mV input for 40W 8 Ohm output
42mV input for 60W 4 Ohm output
- Frequency response:
50Hz to 20KHz -0.5dB; -1.5dB @ 40Hz; -3.5dB @ 30Hz
- Total harmonic distortion @ 1KHz and 8 Ohm load:
Below 0.1% up to 10W; 0.2% @ 30W
- Total harmonic distortion @ 10KHz and 8 Ohm load:
Below 0.15% up to 10W; 0.3% @ 30W
- Total harmonic distortion @ 1KHz and 4 Ohm load:
Below 0.18% up to 10W; 0.4% @ 60W
- Total harmonic distortion @ 10KHz and 4 Ohm load:
Below 0.3% up to 10W; 0.6% @ 60W
- Treble control:
+9 / -16dB @ 1KHz; +12 / -24dB @ 10KHz
- Brightness control:
+6.5dB @ 500Hz; +7dB @ 1KHz; +8.5dB @ 10KHz
- Bass control:
-17.5dB @ 100Hz; -26dB @ 50Hz; -28dB @ 40Hz
Notes:
-
The value listed for C8 is the minimum suggested value. A 3300µF capacitor or two 2200µF capacitors wired in parallel would be a better choice.
-
The Darlington transistor types listed could be too oversized for such a design. You can substitute them with MJ11014 (Q3) and MJ11013 (Q4) or TIP142 (Q3) and TIP147 (Q4).
-
T1 transformer can be also a 24 + 24V or 25 + 25V type (i.e. 48V or 50V center tapped). Obviously, the center-tap must be left unconnected.
-
D1 and D2 can be any Schottky-barrier diode types. With these devices, the harmonic modifier operation will be hard. Using for D1 and D2 two common 1N4148 silicon diodes, the harmonic modifier operation will be softer.
-
In all cases where Darlington transistors are used as the output devices it is essential that the sensing transistor (Q2) should be in as close thermal contact with the output transistors as possible. Therefore a TO126-case transistor type was chosen for easy bolting on the heatsink, very close to the output pair.
-
R9 must be trimmed in order to measure about half the voltage supply from the positive lead of C7 and ground. A better setting can be done using an oscilloscope, in order to obtain a symmetrical clipping of the output waveform at maximum output power.
-
To set quiescent current, remove temporarily the Fuse F1 and insert the probes of an Avo-meter in the two leads of the fuse holder.
-
Set the volume control to the minimum and Trimmer R3 to its minimum resistance.
-
Power-on the circuit and adjust R3 to read a current drawing of about 30 to 35mA.
-
Wait about 15 minutes, watch if the current is varying and readjust if necessary.